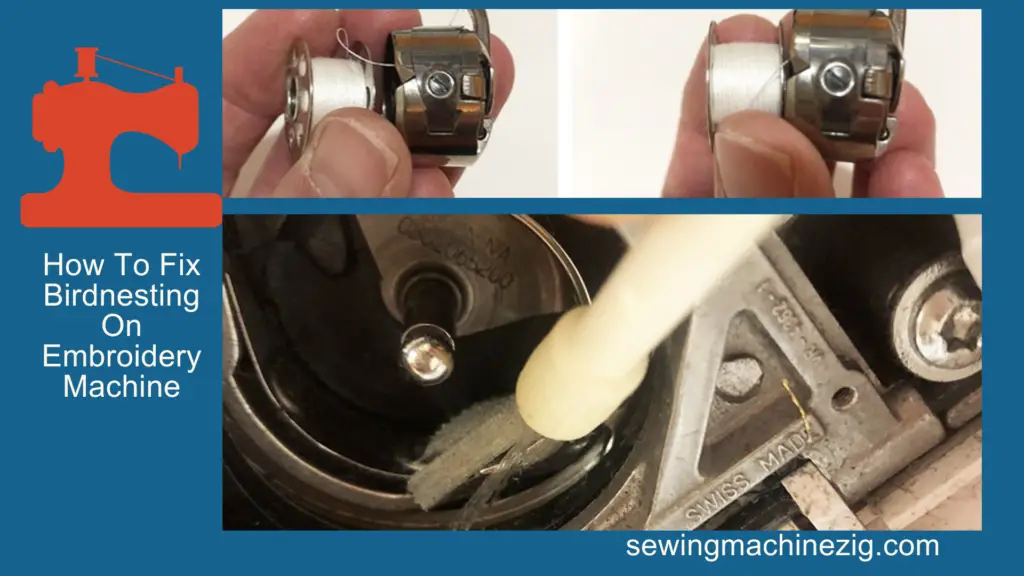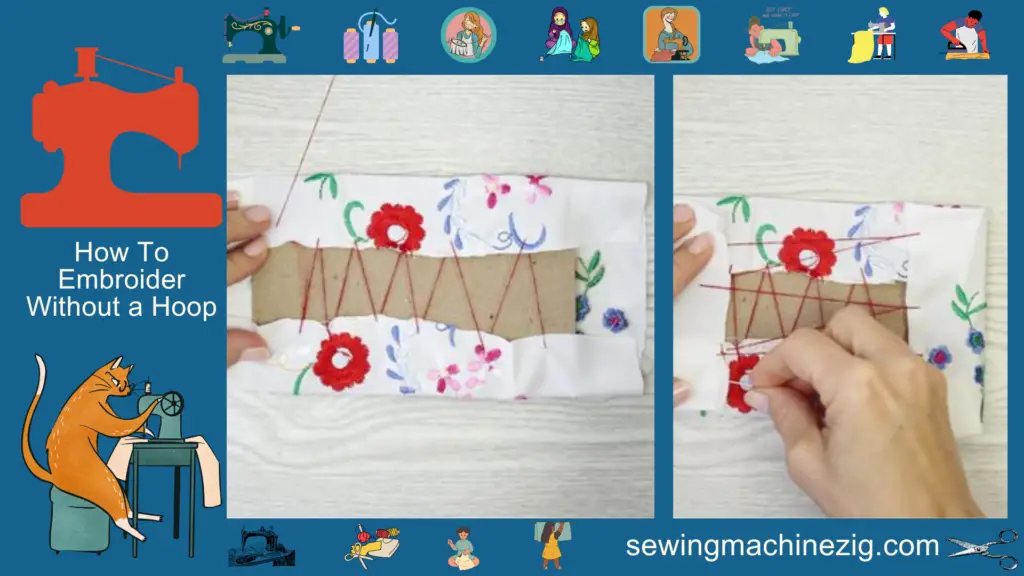
Embroidery is an ancient art form that has been practiced for thousands of years. Its exact origins are difficult to trace, as evidence of early embroidery has not survived well over time.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!However, what is the history of embroidery well archaeological discoveries and historical records provide insights into the rich history of embroidery.
The origins of embroidery can be traced back to ancient civilizations in China, Egypt, Greece, and Persia. It was initially used as a form of embellishment on clothing, textiles, and ceremonial objects.
In many cultures, embroidery was not only a decorative art but also a symbol of wealth, social status, and cultural identity.
During The Middle Ages In Europe
Embroidery flourished as a highly skilled craft. Embroidered garments and tapestries became important status symbols, and skilled embroiderers were in high demand.
The use of gold and silver threads, as well as precious gemstones and pearls, further enhanced the luxurious nature of embroidered works.
In the Renaissance period, learning what is the history of embroidery continued to evolve as a popular form of artistic expression. Intricate designs were created using various stitching techniques, including satin stitch, stem stitch, and couching.
Embroidery became an integral part of fashion, ecclesiastical garments, and home decor.
Embroidery Industrial Revolution In The 18th Century

Embroidery underwent significant changes. The introduction of sewing machines and the mass production of textiles reduced the demand for hand-embroidered goods. what is the history of embroidery in the industrial field; however, embroidery remained a cherished craft practiced by individuals and small workshops.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Arts and Crafts movement revived interest in traditional crafts, including embroidery.
Artists and designers sought to elevate embroidery to the level of fine art, incorporating innovative techniques and exploring new creative possibilities.
Regarding The Invention Of The Embroidery Machine
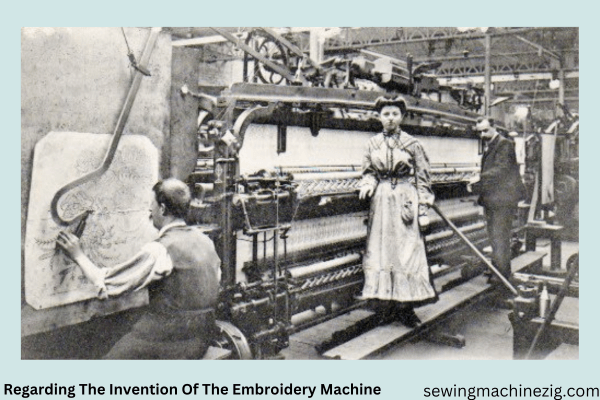
The first notable development in this area occurred in the 19th century. Learning and knowing what is the history of embroidery well the initial machine for embroidery was created by Josué Heilmann in 1804, a Frenchman credited with inventing a hand-embroidery machine.
However, this invention did not achieve significant success or widespread adoption.
The breakthrough in embroidery machine technology came in the mid-19th century with the invention of the Schiffli embroidery machine by Isaak Groebli.
The Schiffli machine, patented in 1863, mechanized the process of embroidery by using multiple needles and a continuously moving fabric, resulting in faster production and more intricate designs.
This invention revolutionized the embroidery industry and let the world understand what is the history of embroidery and marked the beginning of modern machine embroidery.
Evolution In Sewing Machine
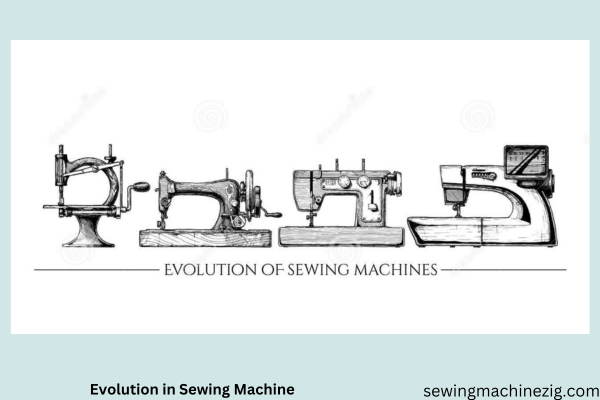
Subsequently, other inventors and manufacturers made significant contributions to the development of embroidery machines. For example, the Singer Sewing Machine Company, founded by Isaac Merritt Singer
Played a crucial role in advancing embroidery technology. Revolute more about what is the history of embroidery in Singer’s company and introduced commercial embroidery machines in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, making machine embroidery accessible to a wider audience.
Since then, embroidery machine technology has continued to evolve rapidly. Today, computerized embroidery machines are widely used, allowing for precise, intricate designs and efficient production.
These machines can read digital embroidery files and automatically stitch patterns with various thread colors and densities.
It’s important to note that what is the history of embroidery invention and development of embroidery machines was the result of cumulative efforts by numerous inventors, engineers, and manufacturers over time.
The contributions of individuals like Heilmann, Groebli, and Singer, among others, have played a significant role in shaping the history and progress of embroidery machines.
Computerized Sewing Machine

Today, embroidery continues to thrive as both a traditional craft and a contemporary art form. Modern technologies have expanded the range of possibilities, what is the history of embroidery computerized machines well as digital embroidery techniques enabling intricate and precise designs?
Embroidery has come a long way since its humble beginnings, evolving from a functional technique to a celebrated form of creative expression. Its rich history and cultural significance have made it a timeless and cherished art form enjoyed by people around the world.
What Was Embroidery Originally Used For

Embroidery, one of the oldest and most enduring forms of decorative art, has a rich history that spans cultures and centuries. From ancient civilizations to the present day, embroidery has served a variety of purposes.
Originally, the embroidery was primarily used for decoration, adorning textiles, garments, and accessories with intricate designs and motifs.
It was a means to enhance the visual appeal of items and showcase the craftsmanship and creativity of artisans.
Over time, embroidery also gained significance in communication, personalization, religious rituals, storytelling, and even functional purposes.
The origins of embroidery and its diverse applications provide a fascinating glimpse into the cultural and artistic traditions of different societies throughout history. Here are some of the primary uses of embroidery and what is the history of embroidery in modern culture.
1. Decoration:
One of the earliest and most common uses of embroidery was for decorative purposes. Embroidered designs were applied to textiles, garments, and accessories to enhance their visual appeal.
Intricate patterns, motifs, and embellishments were stitched onto fabric using different threads, stitches, and techniques.
2. Symbolism And Communication:
Embroidery served as a means of communication and symbolism in many cultures. Embroidered motifs, symbols, and patterns often carried specific meanings, conveying messages or representing cultural, religious, or social affiliations.
Embroidered textiles were used to communicate status, identity, and affiliation within communities.
3. Personalization And Identity:
Embroidery allowed individuals to personalize their belongings and express their identity. Monograms, initials, family crests, or personal designs were often embroidered onto the clothing, linens, and personal accessories to mark ownership and distinguish one from others.
4. Religious And Ceremonial Purposes:
Embroidery played a significant role in religious and ceremonial contexts. Ecclesiastical garments, such as robes, vestments, and altar cloths, were elaborately embroidered to reflect the sacredness and importance of religious ceremonies.
Embroidery was also used in ceremonial clothing for weddings, celebrations, and rituals in different cultures.
5. Storytelling And Narrative:
Embroidery was used as a form of visual storytelling. Historical events, myths, legends, and folktales were often depicted through intricately embroidered scenes and narrative designs.
Embroidered tapestries and textiles served as storytelling mediums, preserving cultural heritage and conveying narratives across generations.
6. Protection And Functionality:
Embroidery was sometimes used for practical purposes as well. Reinforcing seams, mending tears, and strengthening fabric were common applications of embroidery.
In some cases, the embroidery was used to create protective amulets or charms, believed to offer spiritual or magical benefits.
It’s important to note that the specific uses of embroidery varied across different cultures, time periods, and social contexts. However, the universal appeal of embroidery as a form of artistic expression and decoration has endured throughout history.
Where Was Embroidery Born
The exact birthplace of embroidery is challenging to determine, as the practice has ancient origins that developed independently in various regions of the world.
Embroidery can be traced back to different civilizations and cultures throughout history. Some of the earliest evidence of embroidery has been found in ancient China, Egypt, Greece, and Persia.
Embroidery History In China
In China, silk embroidery dates back thousands of years, with early examples discovered from the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BCE).
The Chinese developed intricate techniques and exquisite designs using silk threads, often incorporating gold and silver threads for added luxury.
Embroidery In Egypt
Ancient Egypt also has a rich history of embroidery. Textiles with embroidered motifs have been found in Egyptian tombs dating back to around 3000 BCE.
The Egyptians used embroidery to adorn clothing, accessories, and household items, employing linen threads and incorporating colorful silk and precious metal threads.
Embroidery In Ancient Greece
In ancient Greece, what is the history of embroidery well embroidered textiles were highly valued and played a significant role in their culture. Greek embroidery showcased a variety of techniques, including geometric patterns, mythological scenes, and elaborate borders.
The Greeks used embroidery to embellish clothing, home furnishings, and ceremonial items.
Embroidery In Persia
Similarly, ancient Persia (modern-day Iran) had a strong tradition of embroidery. Persian embroideries were renowned for their intricate designs, vibrant colors, and meticulous craftsmanship.
Embroidery was used to decorate clothing, carpets, and textiles, often featuring floral motifs and intricate patterns.
While these regions are often mentioned in the context of embroidery’s early development, it’s important to note that what is the history of embroidery and embroidery likely emerged independently in many other parts of the world as well.
The craft of embroidery has since spread across continents and cultures, with each region contributing its unique styles, techniques, and artistic expressions.
Conclusion:
The history of embroidery is a testament to the enduring appeal and versatility of this ancient craft. From its origins in ancient civilizations to its evolution into a highly skilled art form, embroidery has played a significant role in human culture and expression.
It has been used for decoration, personalization, communication, storytelling, and functional purposes throughout history. The craft has adapted and thrived, incorporating new techniques, materials, and technologies. Hope now you understand very well what is the history of embroidery.
Today, embroidery continues to captivate with its beauty and intricacy, bridging the past and the present. As artisans and enthusiasts carry on the tradition, the history of embroidery lives on, inspiring creativity and preserving cultural heritage for generations to come.
FAQs:
Q 1: When Did Embroidery First Originate?
A: The exact origins of embroidery are difficult to pinpoint, as it developed independently in different cultures. However, evidence suggests that embroidery dates back thousands of years, with early examples found in ancient China, Egypt, Greece, and Persia.
Q 2: What Materials Were Originally Used For Embroidery?
A: In its early days, the embroidery was predominantly done using natural materials such as animal fibers, plant fibers (like linen), and silk threads. As civilizations progressed, additional materials like gold and silver threads were introduced for more intricate and luxurious designs.
Q 3: How Was Embroidery Traditionally Done?
A: Traditional embroidery involved the use of a needle and thread to stitch decorative designs onto fabric. Different stitches, such as satin stitch, chain stitch, and cross-stitch, were employed to create varied textures and patterns.
Q 4: What Role Did Embroidery Play In Different Cultures Throughout History?
A: Embroidery held diverse significance across cultures. It served decorative purposes, represented status and identity, conveyed symbolic meanings, and was used in religious and ceremonial contexts. Embroidered textiles also functioned as storytelling mediums, preserving cultural narratives.
Q 5: How Did Embroidery Evolve Over Time?
A: Embroidery evolved alongside technological advancements and cultural exchanges. The introduction of embroidery machines in the 19th century mechanized the process, while computerized embroidery machines in modern times have enabled intricate and precise designs.
Q 6: Who Were Some Notable Contributors To The Development Of Embroidery?
A: While the exact inventors of embroidery techniques are unknown, certain individuals played significant roles. Josué Heilmann and Isaak Groebli were early pioneers of embroidery machines, and Isaac Merritt Singer of the Singer Sewing Machine Company contributed to machine embroidery’s advancement.
Q 7: How Has Embroidery Remained Relevant In Modern Times?
A: Embroidery has adapted to contemporary tastes and techniques while maintaining its traditional roots. It has found its place in fashion, art, and craft industries, with artists and enthusiasts incorporating new materials, experimenting with mixed media, and pushing the boundaries of creativity.